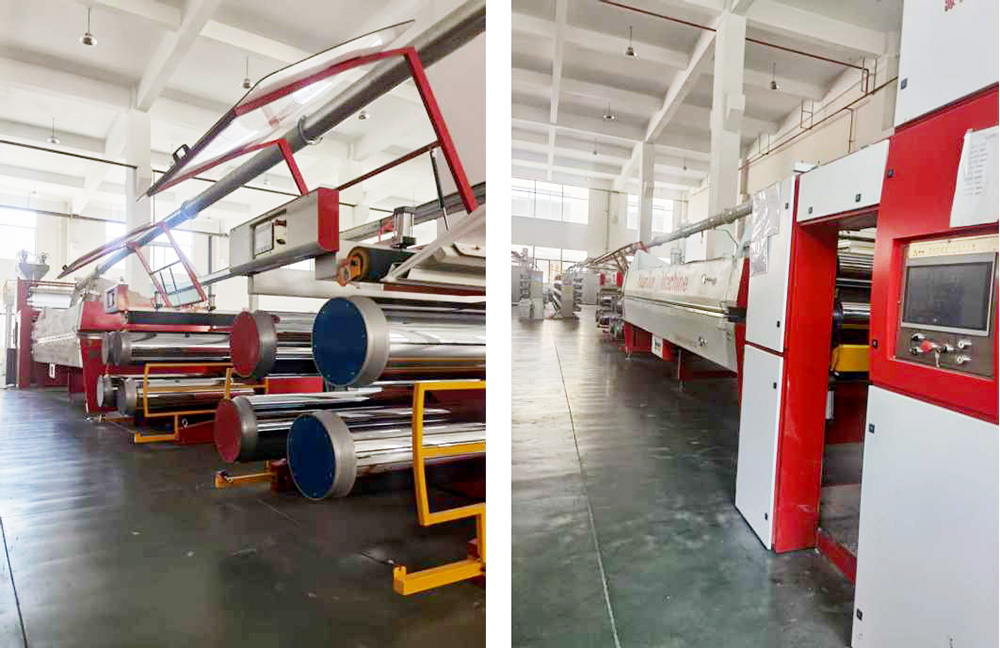
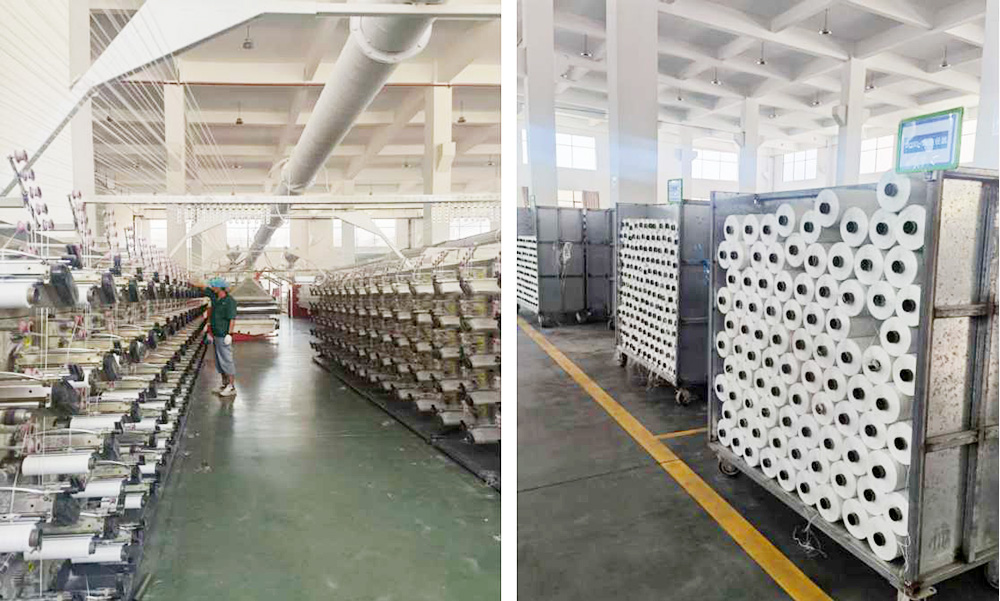
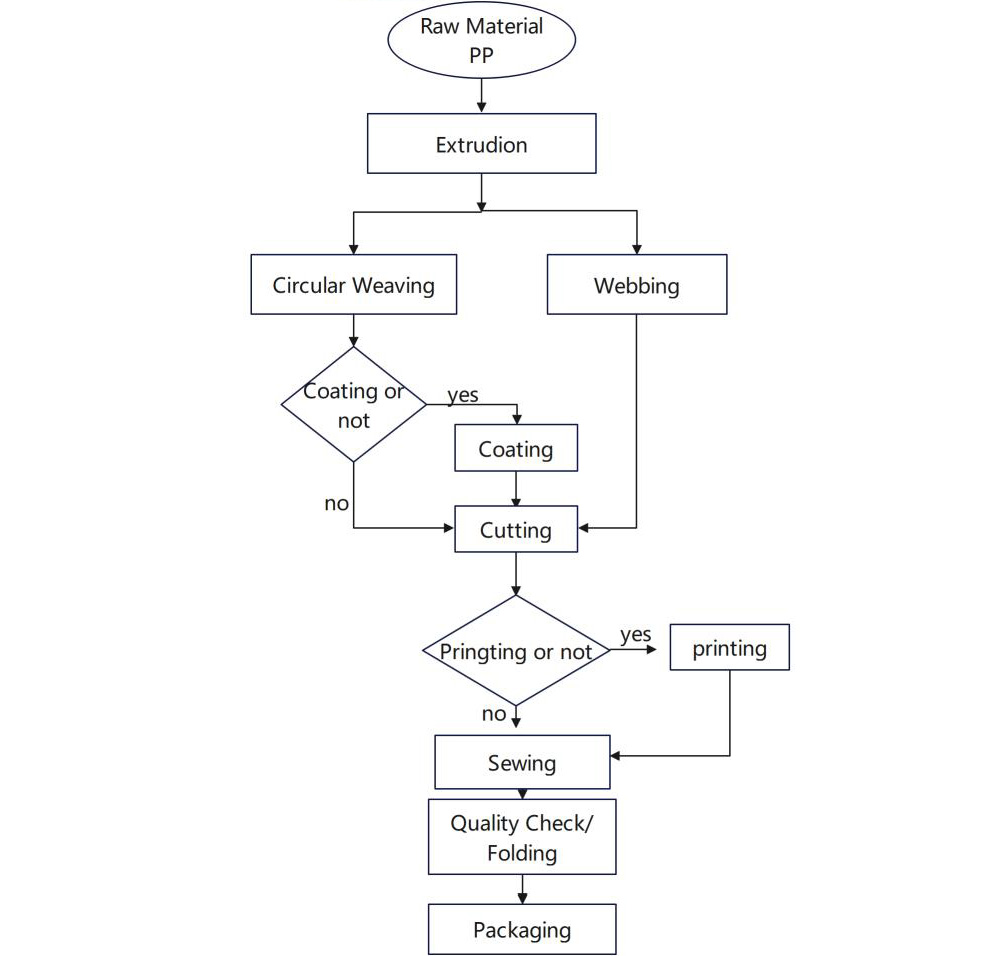



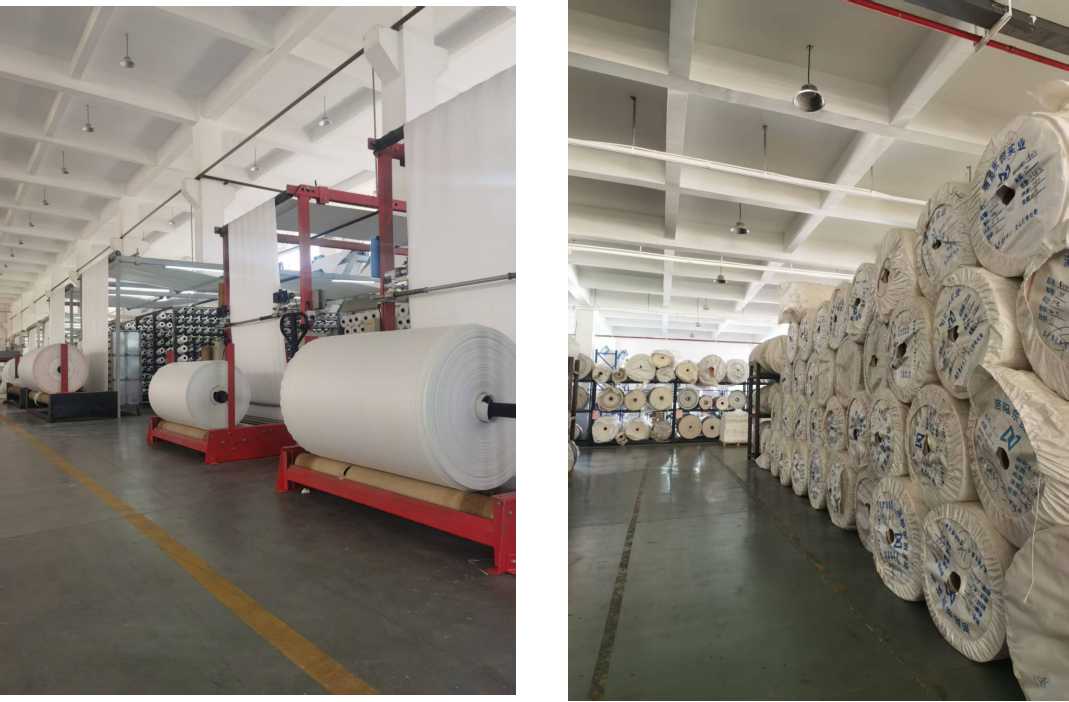
Circular Loom

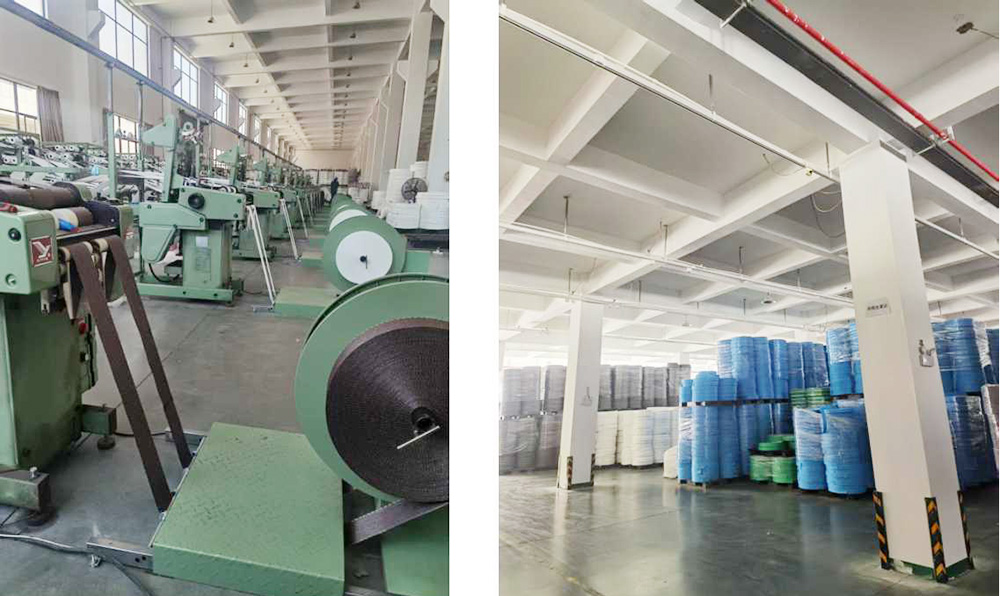
Narrow Weaving

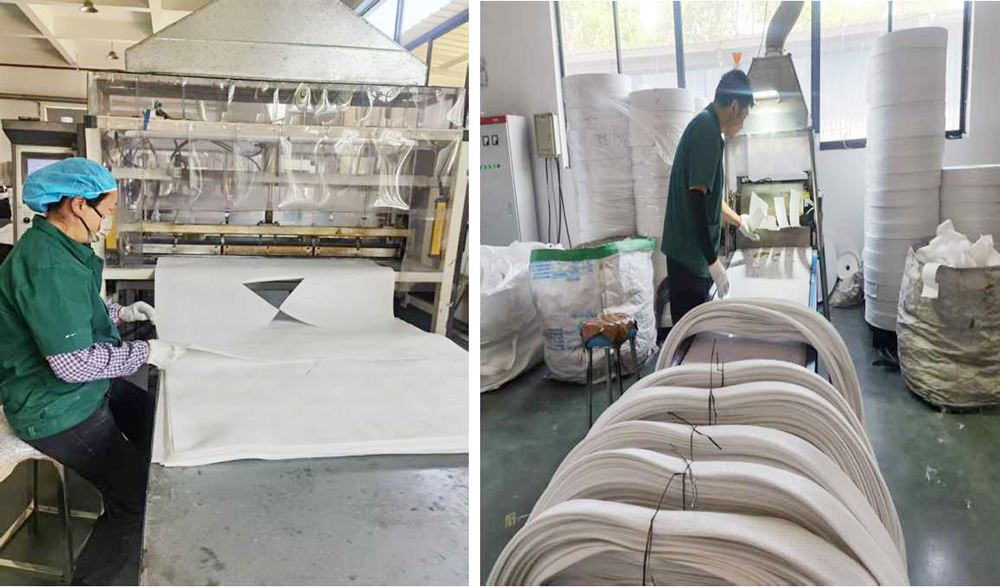
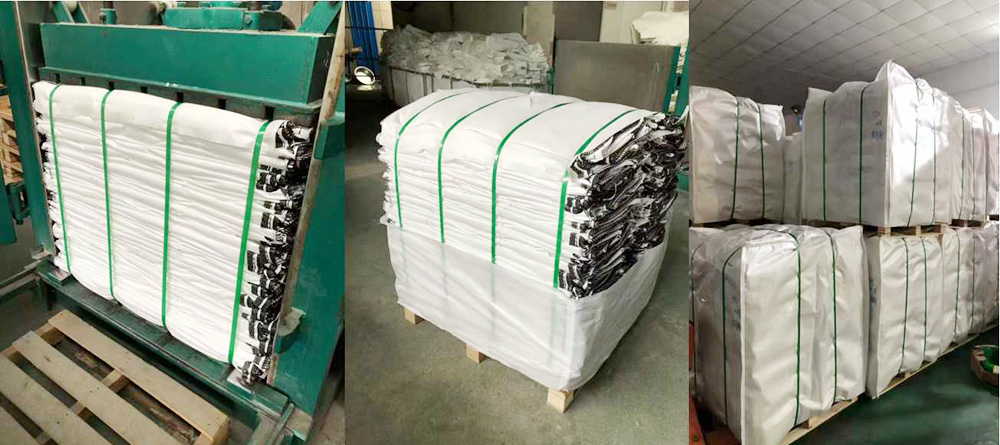
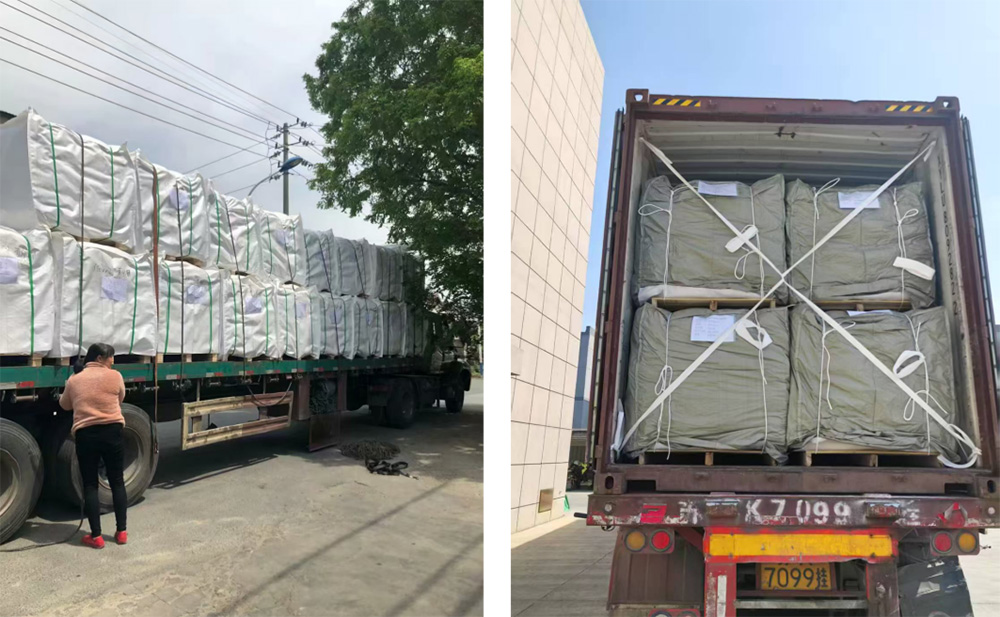
Cutting( Fabric star cut/ Webbing cut)
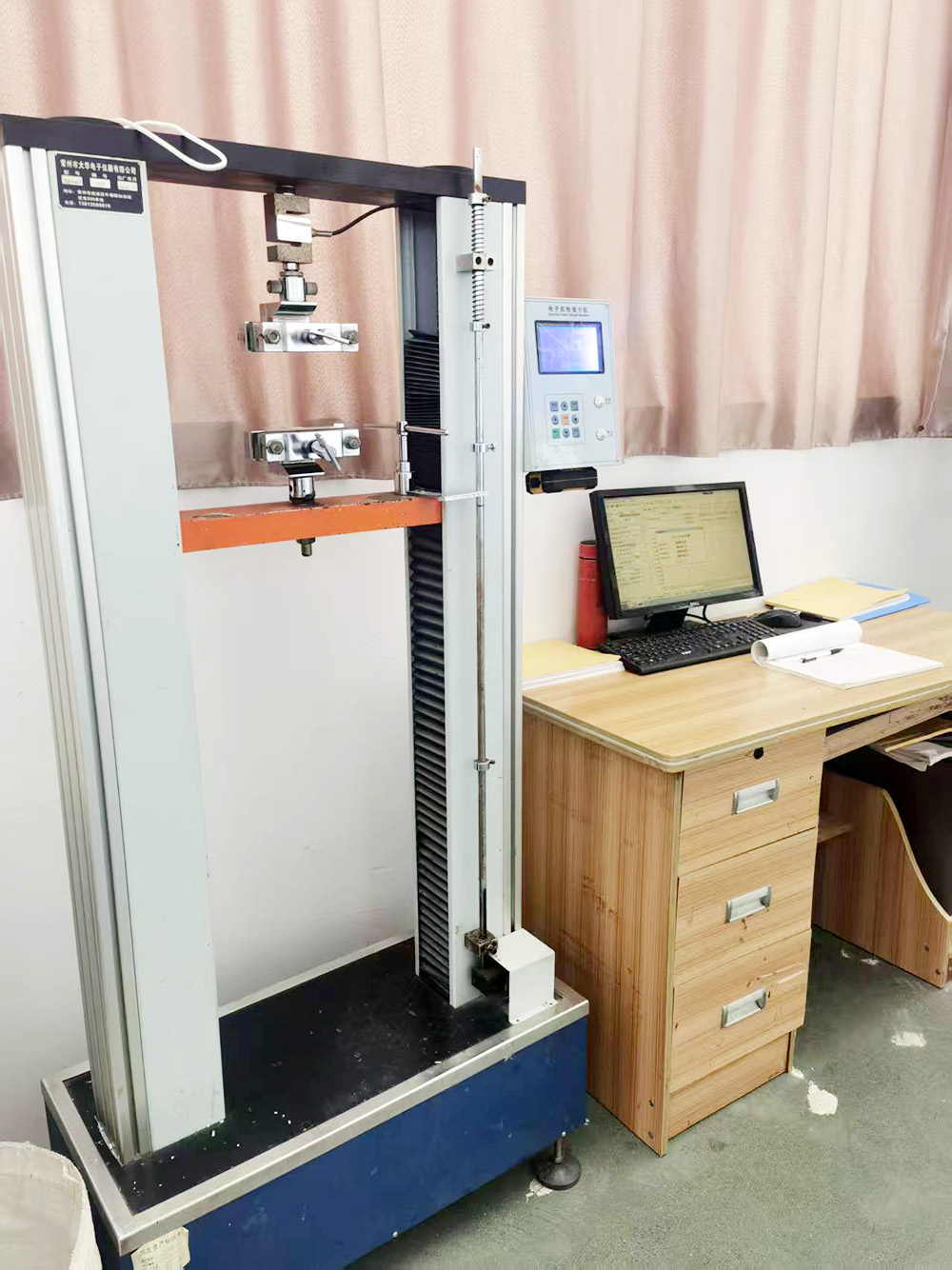






The sling tensile testing machine operates based on the Constant Rate of Extension (CRE) principle. The entire testing process is controlled by a computer. It uses high-precision sensors and measuring systems to real-time collect and convert parameters such as the force and displacement of the specimen during the stretching process into electrical signals. After processing such as amplification and conversion, these signals are transmitted to the computer or display screen and presented in the form of curves or data.
Testing Functions: It can measure the tensile properties of products like slings, such as tensile strength at break and elongation at break. It can also conduct various tests including single yarn stretching, fabric stretching, bursting, and peeling.
Data Processing: It is capable of recording dynamic changes in curves as well as data such as tensile strength at break, elongation at break, time, and number of cycles.
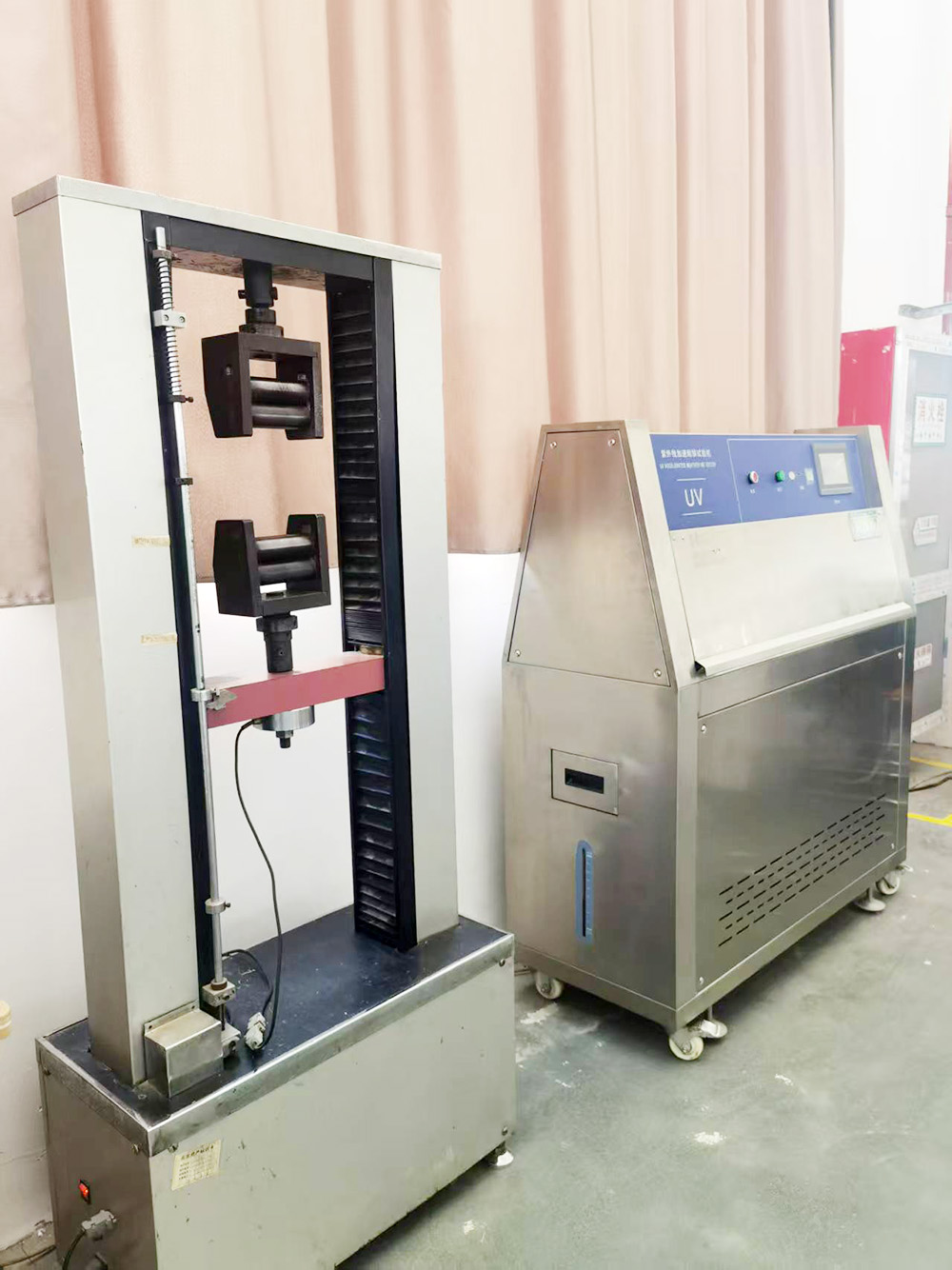

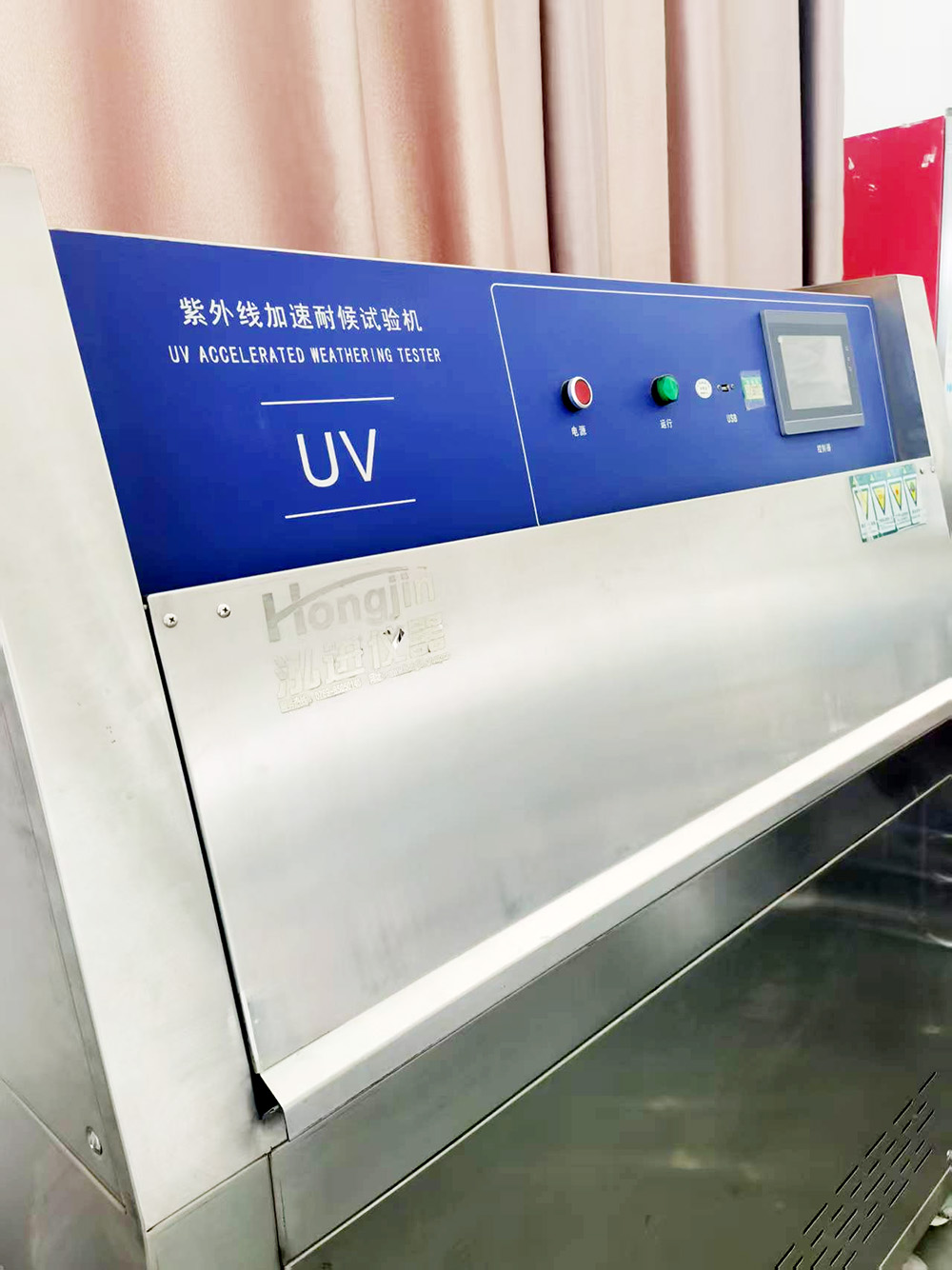
The UV accelerated weathering test chamber is a testing device used to simulate conditions such as UV radiation, high temperature, and high humidity found in natural environments, in order to accelerate the assessment of the weathering performance of materials or products.
UV Radiation: The device is equipped with special UV fluorescent lamps inside, which emit UV wavelengths similar to those in natural sunlight, capable of simulating the destructive effects of UV rays from sunlight on materials.
Temperature Control: The test chamber can set a high-temperature environment, typically ranging from 40°C to 80°C, to simulate the aging reactions of materials under high-temperature conditions.
Humidity Control: Through spray or humidification systems, it simulates the humid conditions in natural environments, accelerating the hydrolysis and corrosion processes of materials.
Condensation Cycle: Some devices are also equipped with a condensation cycle system, which forms a water film on the inner surface of the test chamber through condensation water, simulating the erosive effects of dew on materials.
